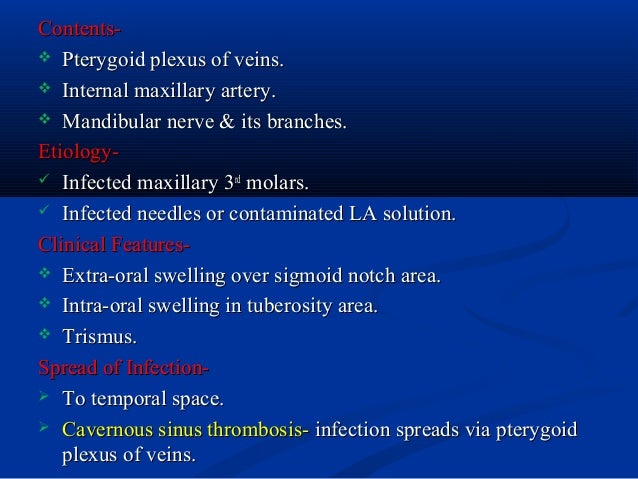
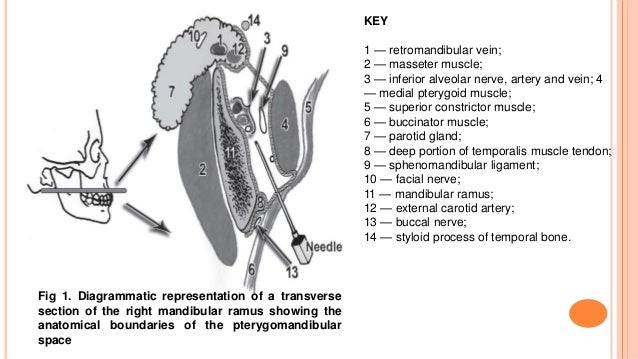
5 it is bounded medially and inferiorly by the medial pterygoid muscle 7 and laterally by the medial surface of the mandibular ramus.
Roof of pterygomandibular space is formed by.
Anatomic boundaries the boundaries of each pterygomandibular space are.
Which of the following spaces is considered by healthcare professionals to be the danger space of the neck.
It is a potential space in the head and is paired on each side.
It is located between the medial pterygoid muscle and the medial surface of the ramus of the mandible.
The roof of pterygomandibular space is formed by.
Which of the following muscles forms the roof of the pterygomandibular space.
Medial pterygoid muscle c.
Trismus associated with the infection of lateral pharyngeal space is related to irritation of the a.
4 lateral pterygoid muscle.
The pterygomandibular space is a fascial space of the head and neck.
The roof of pterygomandibular space is formed by.
The roof of pterygomandibular space is formed by.
Medial pterygoid muscle c.
Comprehending maxillofacial anatomy and related pathology with cbct.
The roof of pterygomandibular space is formed by a.
Lateral pterygoid retropharyngeal space infection is mainly due to spread of.
2 temporalis muscle.
Which of the following muscles forms the roof of the pterygomandibular space.
The roof of pterygomandibular space is formed by.
Retropharyngeal space infection is mainly du.
The pterygomandibular space is a small fascial lined cleft containing mostly loose areolar tissue.
Trismus associated with infection of lateral pharyngeal space is related to.
1 cranial base.
Lateral pterygoid muscle b.
Which of the following blood vessels is located within the sublingual space.
The week in review.
Posteriorly parotid glandular tissue curves medially around the back of the mandibular ramus to form a posterior border while anteriorly the buccinator and superior constrictor muscles come together to form a fibrous junction the pterygomandibular raphe.
The pterygomandibular raphe anteriorly the parotid gland deep lobe posteriorly the lateral pterygoid muscle superiorly the inferior border of the mandible lingual surface inferiorly the medial pterygoid muscle medially the space is superficial to the medial pterygoid the ascending ramus of the mandible laterally the space is deep to the ramus of the mandible o anteriorly the buccinators and superior constrictor.
Oral medicine and radiology oral pathology and microbiology 1 more identify this hand instrument.
E to spread of.
3 medial pterygoid muscle.